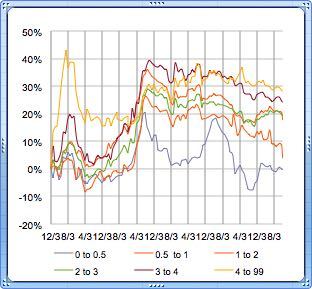
Natural Diamond Prices – July 2025
PriceScope delivers monthly insights into the natural diamond market for consumers, traders, and industry professionals. This July report captures the latest shifts in pricing trends across premium, mid-range, and lower-grade…