strmrdr
Super_Ideal_Rock
- Joined
- Nov 1, 2003
- Messages
- 23,295
Note dont take the comments in this post as facts Im mearly throwing out my understanding of the issue for discussion :}
Contrast Brilliance is the difference between the dark areas of a diamond and the bright areas. The more contrast the brighter the diamond appears for any given amount of total light return.
The darker the dark areas are compared to the light areas the brighter it appears.
Diamonds achieve contrast is 3 ways.
Leakage:
Examples of this are asschers that use leakage to define the patterns the diamonds are famous for showing.
Crushed ice looking radiants are another example.
Near the girdle area of h&a diamonds not specifically cut to eliminate it are another example.
Light redirection:
The light is returned at a different angle than the main light return.
This can be seen as blacks in idealscope images of h&a diamonds and is even more obvious in the new AGS aset scope images.
The arrows in h&a diamonds are examples of light redirection contrast.
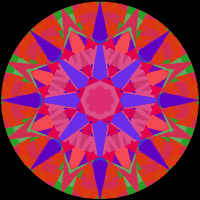
"AGS has an Angular Spectrum Evaluation Tool or ASET (they pronounce it ‘asset’). The images are much like IS but use different colors to show light returned at different angles. White is leakage, green is from 0 to 45 degrees from the horizon, red is from 45 to 75 degrees, and blue is 75 to 90 degrees."
Mirror:
The third way of achieving contrast is to act as a flat mirror and reflect back the object that is in front of it for the dark areas while returning light for the bright areas.
“head shadow” that is talked about often here is an example of this.
Often times light redirection will appear as acting as a mirror the primary light return is directed away but the secondary reflection show up as a reflection of the environment around the diamond.
Contrast Brilliance is the difference between the dark areas of a diamond and the bright areas. The more contrast the brighter the diamond appears for any given amount of total light return.
The darker the dark areas are compared to the light areas the brighter it appears.
Diamonds achieve contrast is 3 ways.
Leakage:
Examples of this are asschers that use leakage to define the patterns the diamonds are famous for showing.
Crushed ice looking radiants are another example.
Near the girdle area of h&a diamonds not specifically cut to eliminate it are another example.
Light redirection:
The light is returned at a different angle than the main light return.
This can be seen as blacks in idealscope images of h&a diamonds and is even more obvious in the new AGS aset scope images.
The arrows in h&a diamonds are examples of light redirection contrast.

"AGS has an Angular Spectrum Evaluation Tool or ASET (they pronounce it ‘asset’). The images are much like IS but use different colors to show light returned at different angles. White is leakage, green is from 0 to 45 degrees from the horizon, red is from 45 to 75 degrees, and blue is 75 to 90 degrees."
Mirror:
The third way of achieving contrast is to act as a flat mirror and reflect back the object that is in front of it for the dark areas while returning light for the bright areas.
“head shadow” that is talked about often here is an example of this.
Often times light redirection will appear as acting as a mirror the primary light return is directed away but the secondary reflection show up as a reflection of the environment around the diamond.








300x240.png)