How Are Diamonds Made? Natural vs Lab-Created Explained
Two Paths, One Diamond Not all diamonds come from the same place — but they all start the same way. Pure carbon, crystalized under immense pressure and heat. Whether it…
The round brilliant diamond is the most popular diamond shape, by far.
Before going on: Check out the PriceScope Diamond Buying Guide
Want the best round cut diamonds? Our elite list of vetted vendors like Whiteflash and James Allen are experts at listening and helping you determine which shape and combo of the 4Cs is perfect for you - and nicely in budget.
The round cut diamond reigns as the most beloved among all diamond shapes, capturing the hearts of gem enthusiasts worldwide. An impressive 90% of all gem-quality diamonds are fashioned into modern round brilliants. This preference stems from two key considerations:
Efficient Use of Material: Diamond producers prioritize the efficient utilization of each crystal. Cutting two round cut diamonds from a single rough stone often maximizes yield, making it a favored approach in diamond cutting.
Optimal Light Performance: The round diamond, when expertly cut, excels at reflecting light back to the observer’s eyes, enhancing its brilliance and fire. This shape is engineered to optimize light return, although the drive to preserve carat weight can sometimes lead to compromises in cut quality.
Despite the occasional focus on weight over aesthetics, the round cut diamond remains a symbol of elegance and radiant beauty, perfect for those seeking both tradition and exceptional sparkle in their jewelry.
PriceScope Pointer: Unlike color and clarity grades, laboratory cut grades are EXTREMELY LIBERAL. For example, more than 60% of round brilliants earn the GIA Excellent cut grade, even though most of those suffer from light leakage, brightness reduction and poor spread. Read more on our page about Diamond Cut.
Diamonds are composed of flat polished surfaces called facets, arranged in specific patterns. The modern round cut diamond is faceted in the brilliant style, using kite-shaped surfaces to enhance sparkle. The modern round brilliant is typically composed of 57 facets we divide into 3 main parts. Essentially top, middle and bottom, these are the Crown, Girdle, and Pavilion.
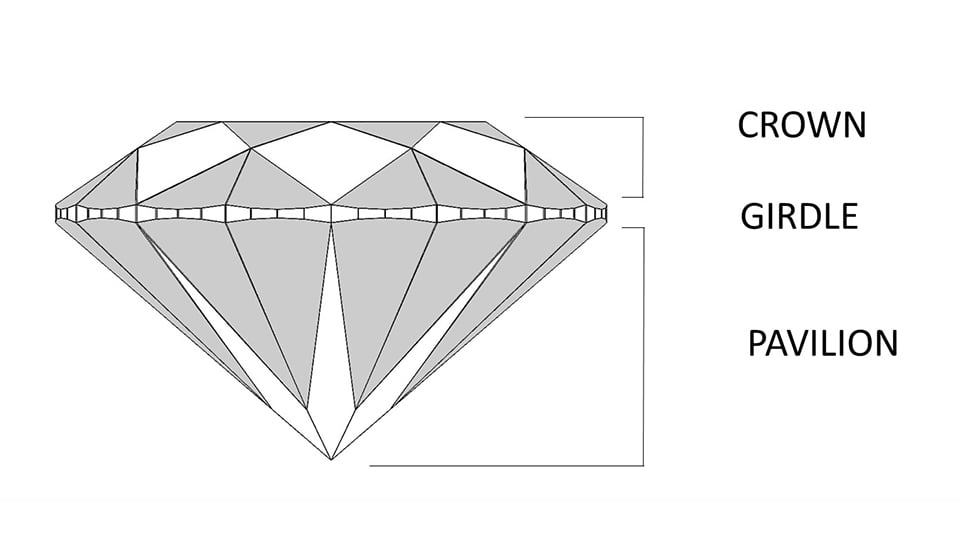
The Crown is the top part of the round diamond, above the girdle. Light enters the diamond through its crown.
The Girdle is like a belt, providing separation between the crown and the pavilion, which would otherwise come together as a sharp edge.
The Pavilion is the bottom part of the round diamond, below the girdle. The pavilion facets should reflect light that has entered through the crown facets so that it returns to the viewer.
Looking for expert advice before purchasing your round cut diamond? Join the PriceScope community to connect with fellow enthusiasts and industry professionals.
Discover the unparalleled brilliance of Whiteflash’s A Cut Above® Round Brilliant Diamonds. Each diamond in this exclusive collection is a testament to Whiteflash’s commitment to excellence, featuring superb craftsmanship and a cut precision that maximizes sparkle and light performance.
These diamonds are not just stones; they are the result of meticulous attention to detail and a passion for perfection. Chosen by hand to ensure they meet stringent quality standards, A Cut Above® diamonds offer a sparkle so intense, they truly stand apart in the world of fine jewelry. Whether set in a timeless engagement ring or a stunning pendant, these diamonds make every moment and memory shine brighter.
Shopping for engagement ring settings? Browse PriceScope’s collection of natural and lab-grown diamond engagement rings from industry leaders such as Adiamor and B2B Jewels.
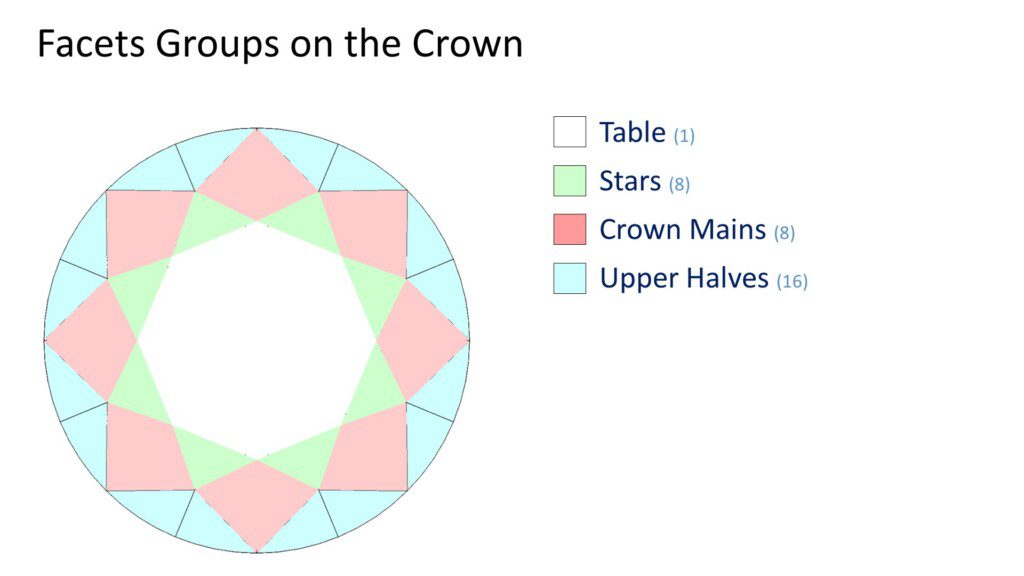
There are eight facet groups on a modern round brilliant diamond. Each group has a different role to play in determining how bright and lively the diamond will be.
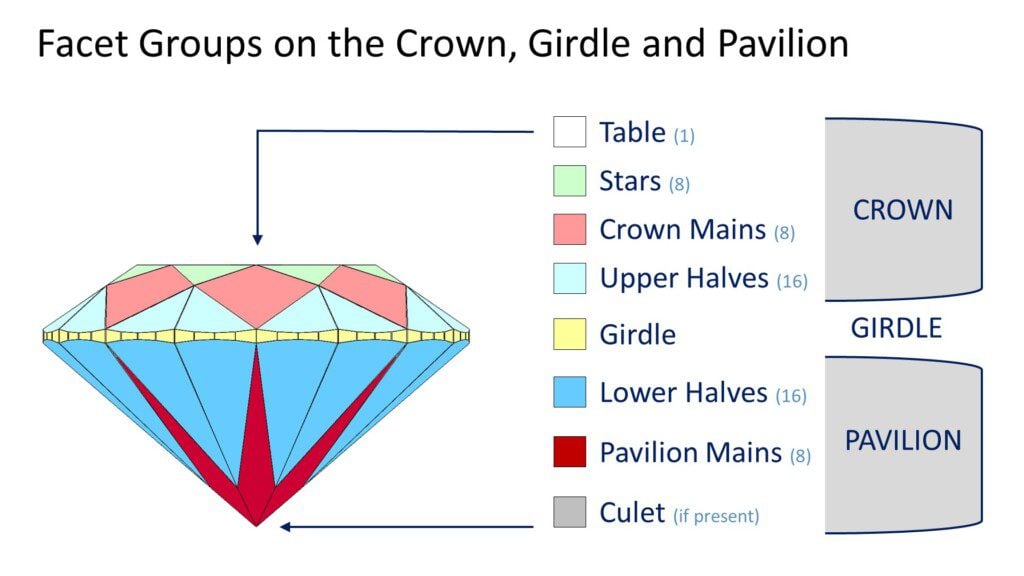
Table: This is a single facet, the largest on the round cut diamond. Octagonal in shape, it sits at the top of the crown.
Stars: The star facets are eight triangular facets extending from the table to the upper half (upper girdle) facets.
Crown Mains: Often referred to as “bezel facets,” the crown mains are eight kite shaped facets connect the table to the girdle. They are twins to the Pavilion Main facets beneath them.
Upper Halves: Also known as “upper girdle facets,” the 16 triangular upper half facets connect the girdle to the base of the star facets. They are twins to the Lower Half facets beneath them.
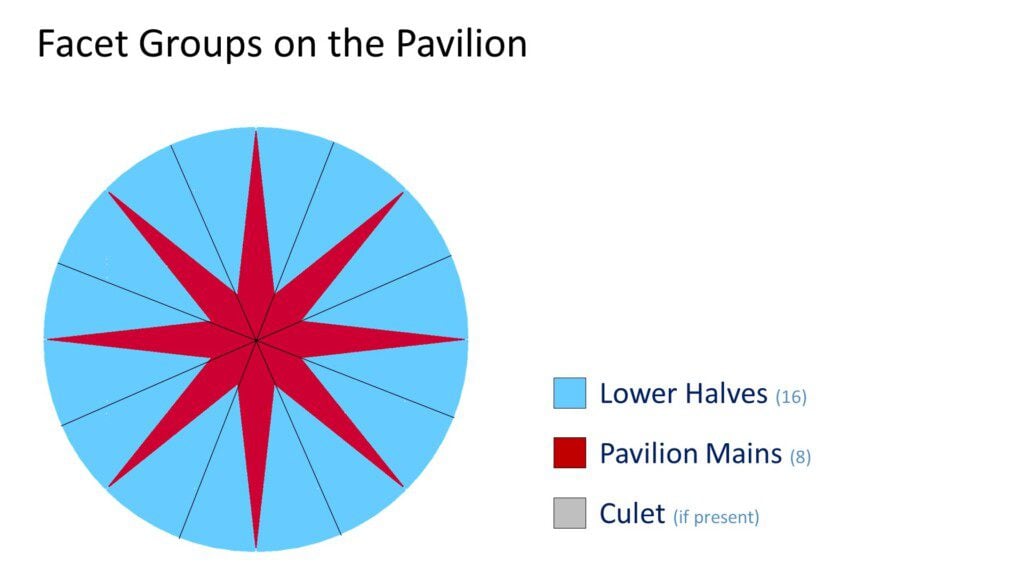
Girdle: The girdle separates the round diamond’s crown and pavilion. The girdle may be polished with tiny facets, semi-polished, or (rare in modern times) left rough.
Lower Halves: Also known as “lower girdle facets,” the 16 triangular lower half facets extend from the bottom of the girdle toward the culet. Their length determines how wide the pavilion main facets will be.
Pavilion Main Facets: These eight kite shaped facets extend from the girdle all the way to the culet. These facets are the primary drivers of light return, when properly paired with other key facet groups.
Culet (if present): A properly produced modern round diamond will not have a culet. The bottom of the diamond should come to a sharp point where the pavilion mains meet. If that does not happen a small “culet” facet will be polished at the bottom. If a culet facet is present the round cut diamond will have 58 facets, instead of the usual 57.
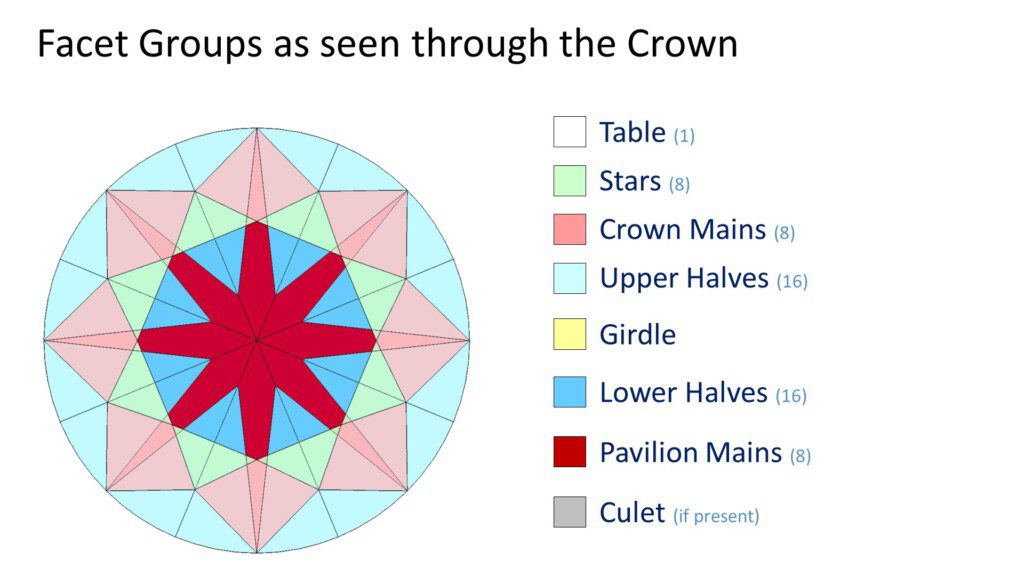
The physics of light-behavior within a round cut diamond are reliably consistent, which means proportions can be used to draw certain conclusions about a round diamond’s cut-quality and likely appearance.
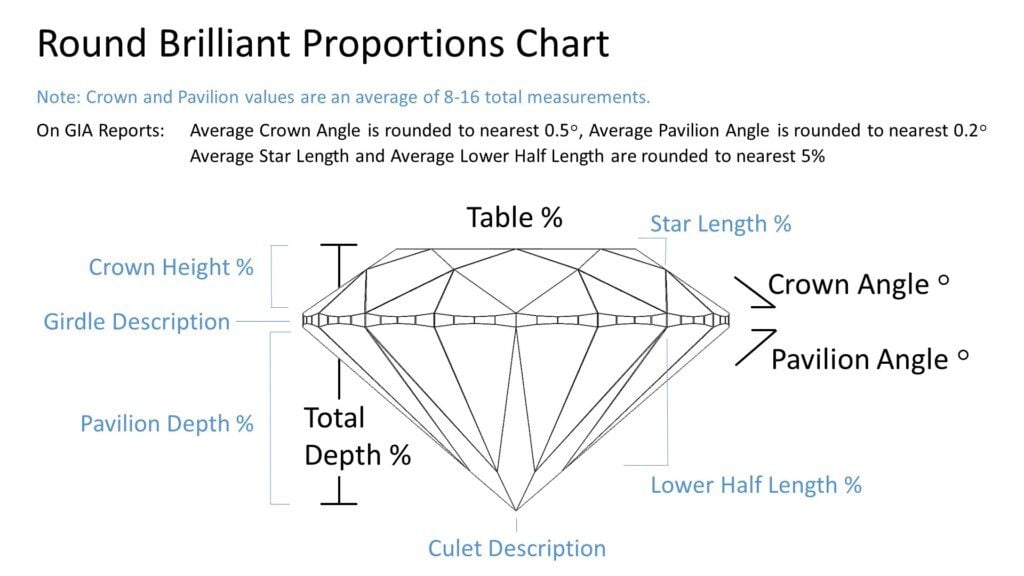
Note: Most data points on a grading report are averages of eight or sixteen measurements. For a round cut diamond this means a pavilion angle of 40.8 could be the average of eight very precisely cut pavilion-facets ranging from (example) a minimum of 40.6 to a maximum of 41.0. Or those eight facets could have a much wider variance from (example) min 40.3 to max 41.3 (or wider), creating potential performance deficits.
On GIA Reports: The numbers are not accurate to the tenth of a degree, like they are on AGS reports. For a round diamond the pavilion angle will be rounded to the nearest 0.2 degrees. The crown angle, star and lower halves are rounded to nearest 0.5 degree or 5%. This can interfere with those wanting extremely detailed round diamond analysis.
Summary: Proportions measurements are useful for a round cut diamond when using broad predictive analysis tools such as the Holloway Cut Advisor. But the nature of averaged and potentially rounded values – standing for 8-16 separate measurements apiece – cannot be used to predict the diamond’s cut consistency, 3D optical precision or performance flavor nuance, for those seeking such analysis.
Why wait for the perfect round cut diamond? Explore PriceScope’s handpicked selection of lab-grown and natural diamond jewelry, ready to adorn your collection from top brands like James Allen and Blue Nile.
Get fast answers to any question: Ask our community of unbiased independent helpers.
Ready to find your diamond?
Retail Diamond Prices Chart Updated Monthly.

Two Paths, One Diamond Not all diamonds come from the same place — but they all start the same way. Pure carbon, crystalized under immense pressure and heat. Whether it…
A Wedding Ring as Unique as Your Love Finding the right wedding ring isn’t just about diamonds or gold – it’s about finding the one that feels right. With hundreds…
So, you’re thinking about lab-grown diamonds? Smart move. They’re just as sparkly as the natural kind but usually cost less. But where do you actually go to buy them? It…

Want to stay updated on the most recent blogs, forum posts, and educational articles? Sign up for Bling News, PriceScope’s weekly newsletter.